Maxwell Quasi Static
This section presents the Maxwell Quasi Static (MQS) model with associated test cases :
-
General Case : Presents the Maxwell equation and the A-V Formulation
-
MQS + gauge condition : Presents the A-V Formulation with gauge condition
-
Test Case Static : Presents the Test Case of Static case with CFPDEs
-
Test Case : Presents the Test Case of Transient case with CFPDEs
-
Test Case Two Tores : Presents the Test Case of Transient case with CFPDEs for geometry of Two Tores
-
-
Two Dimensions Case : Presents the A-V Formulation in two dimensions
-
Axisymmetrical Case : Presents the A-V Formulation in axisymmetrical coordinates
-
Test Case Magnetostatic : Presents the Test Case of Static case with CFPDEs
-
Test Case : One Torus : Presents the Test Case of Transient case with CFPDEs
-
Test Case : Two Tores : Presents the Test Case of Transient case with CFPDEs for geometry of Two Tores
-
The goal of LNCMI is to reach great magnetic field for experiments. To do that, the laboratory use some technologies :
Resistive magnet, it composed by resistive magnet, it loses electric energy by Joules Effect. There are two type of geometry :
-
Helix : It is a superposition of double helix. The more helices are added inside, the bigger the magnetic field but the smaller the experimental space. It used in the center and are more resistant. The helices are composed by copper and silver alloying.
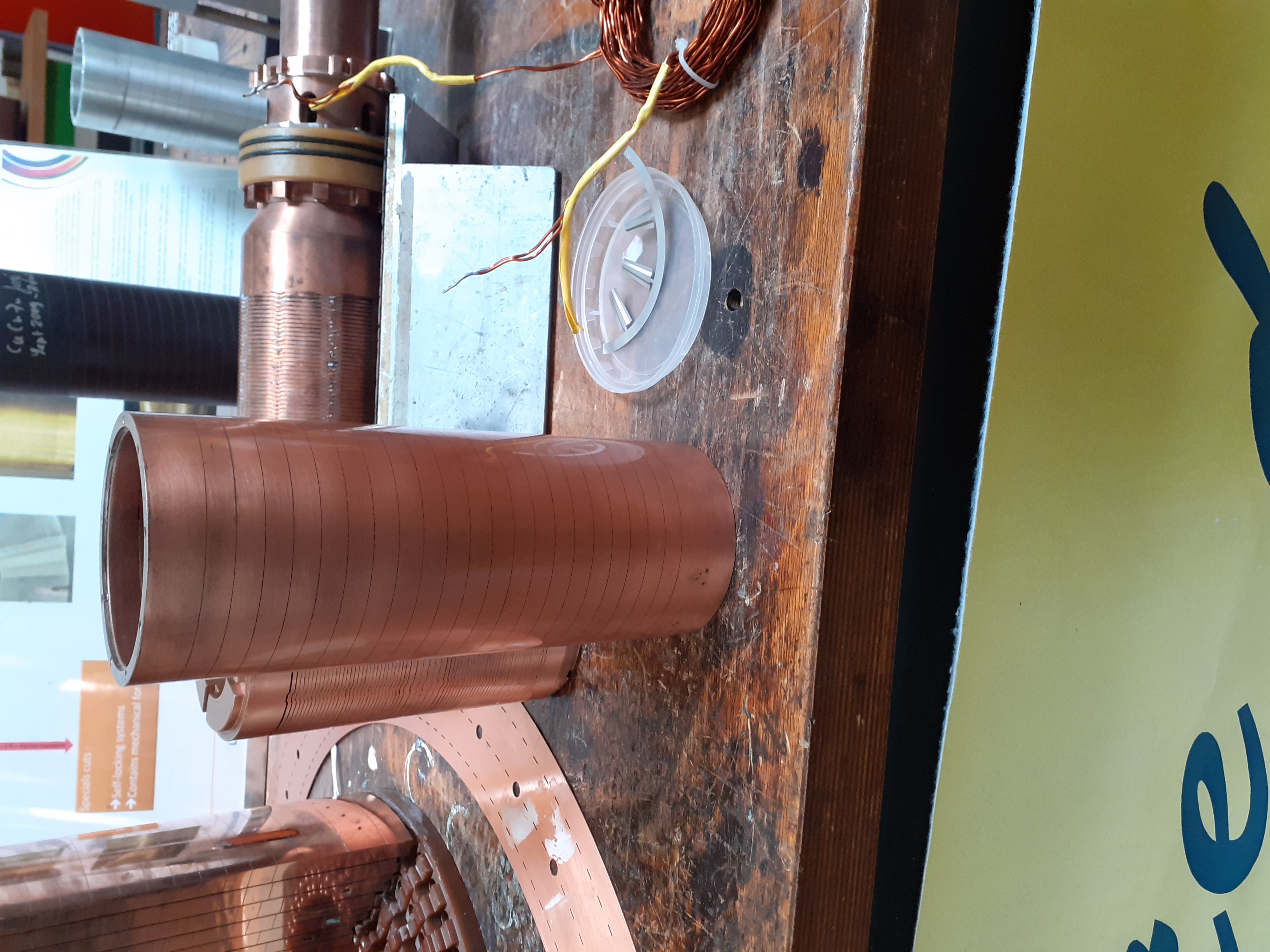

One Helix
|
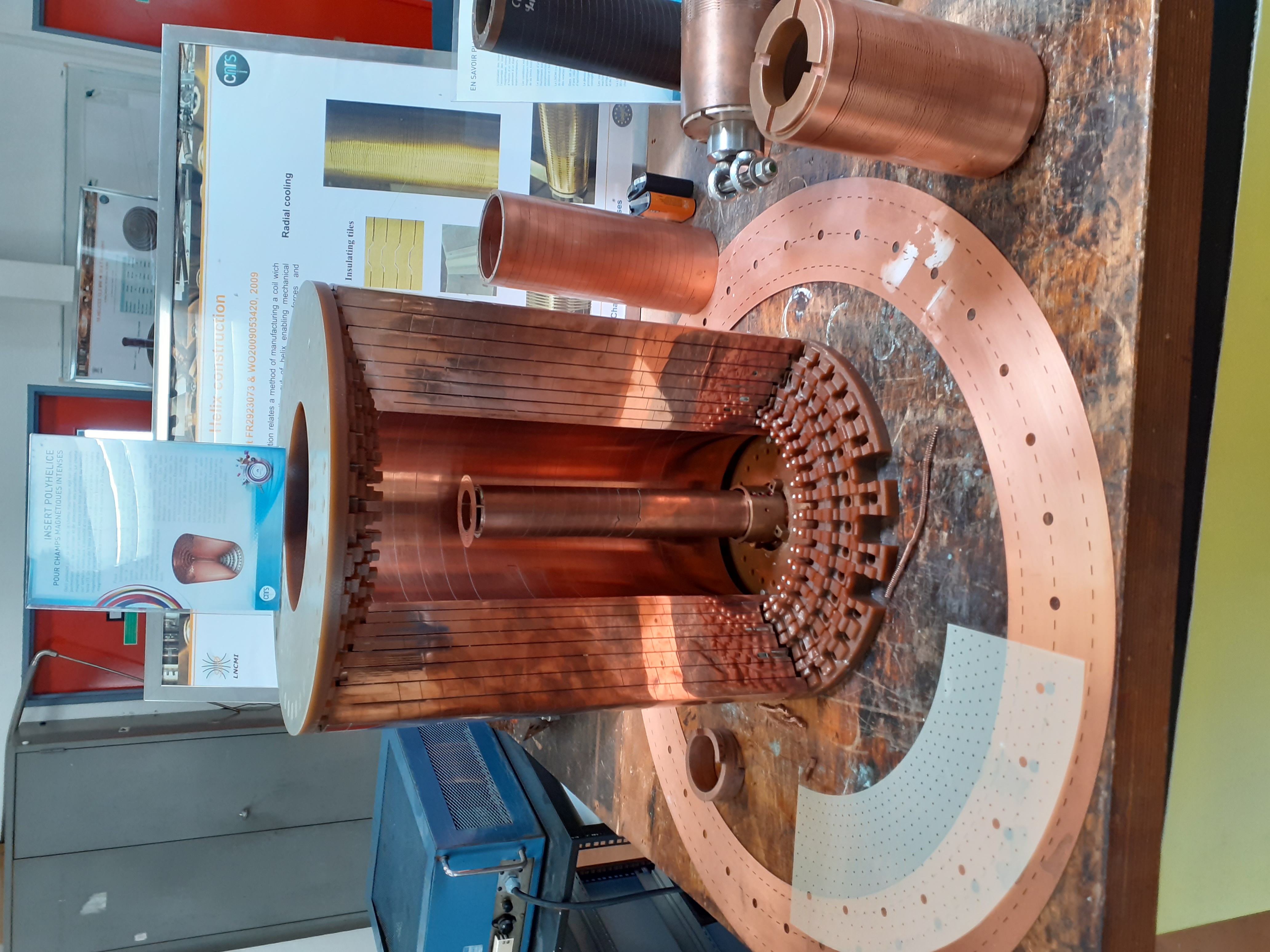

Interior of Helixes
|
||||||||||
|
-
Bitter : It is superposition of copper circle cut in on radius and joined each other to form helix. An electrical insulator are placed between two circles.
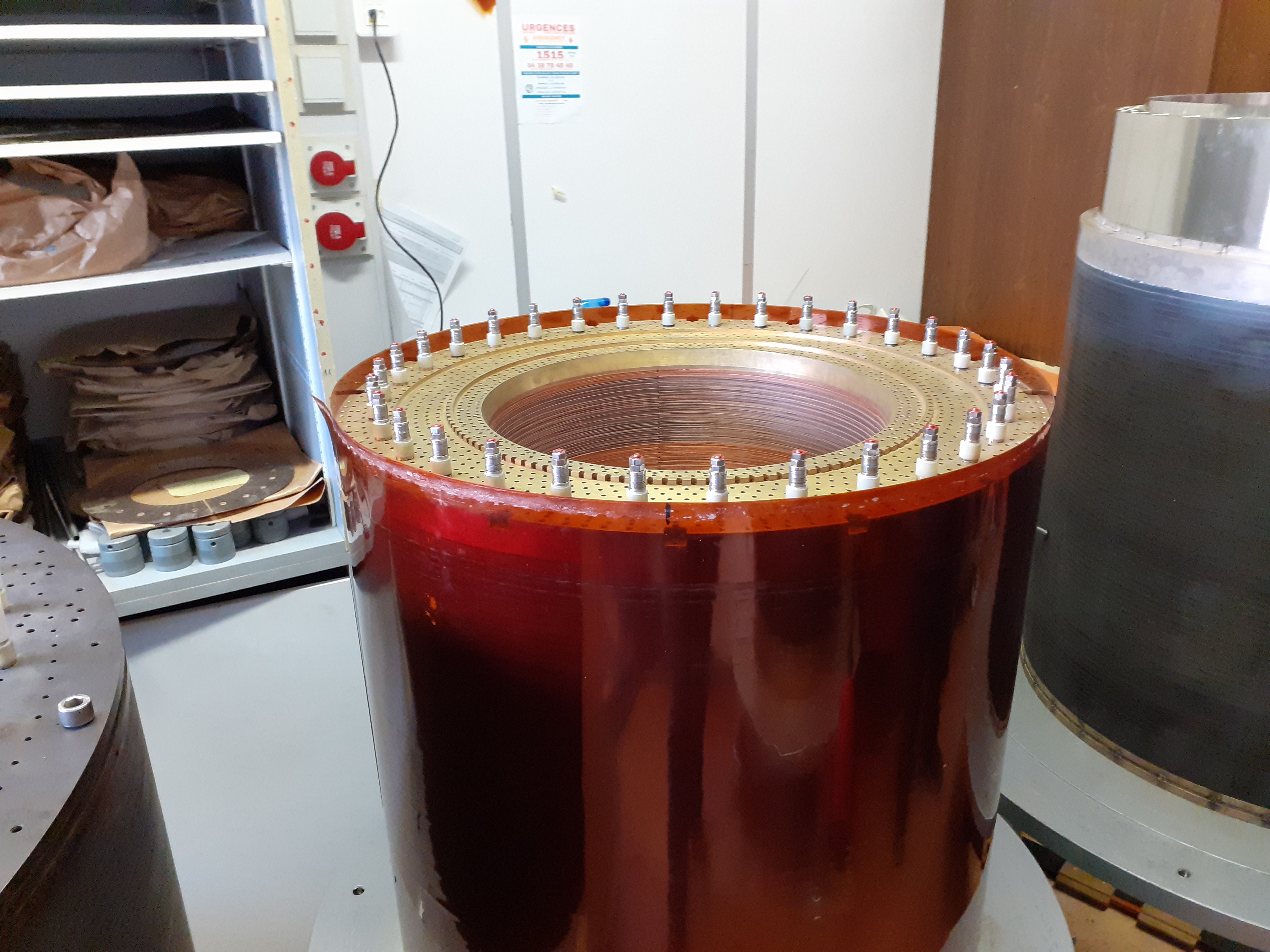

Bitter Magnet
|
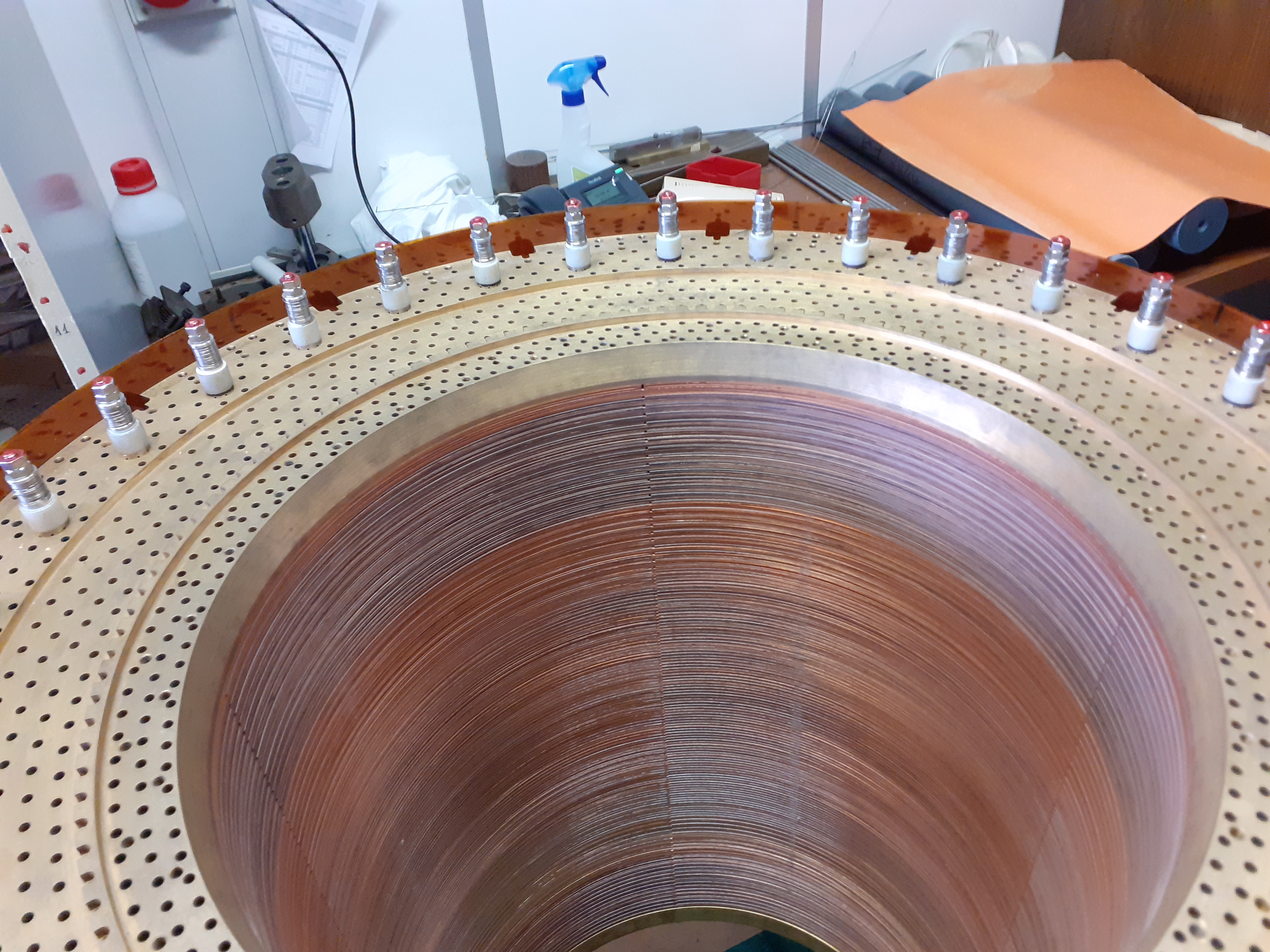
Interior of Bitter Magnet
|
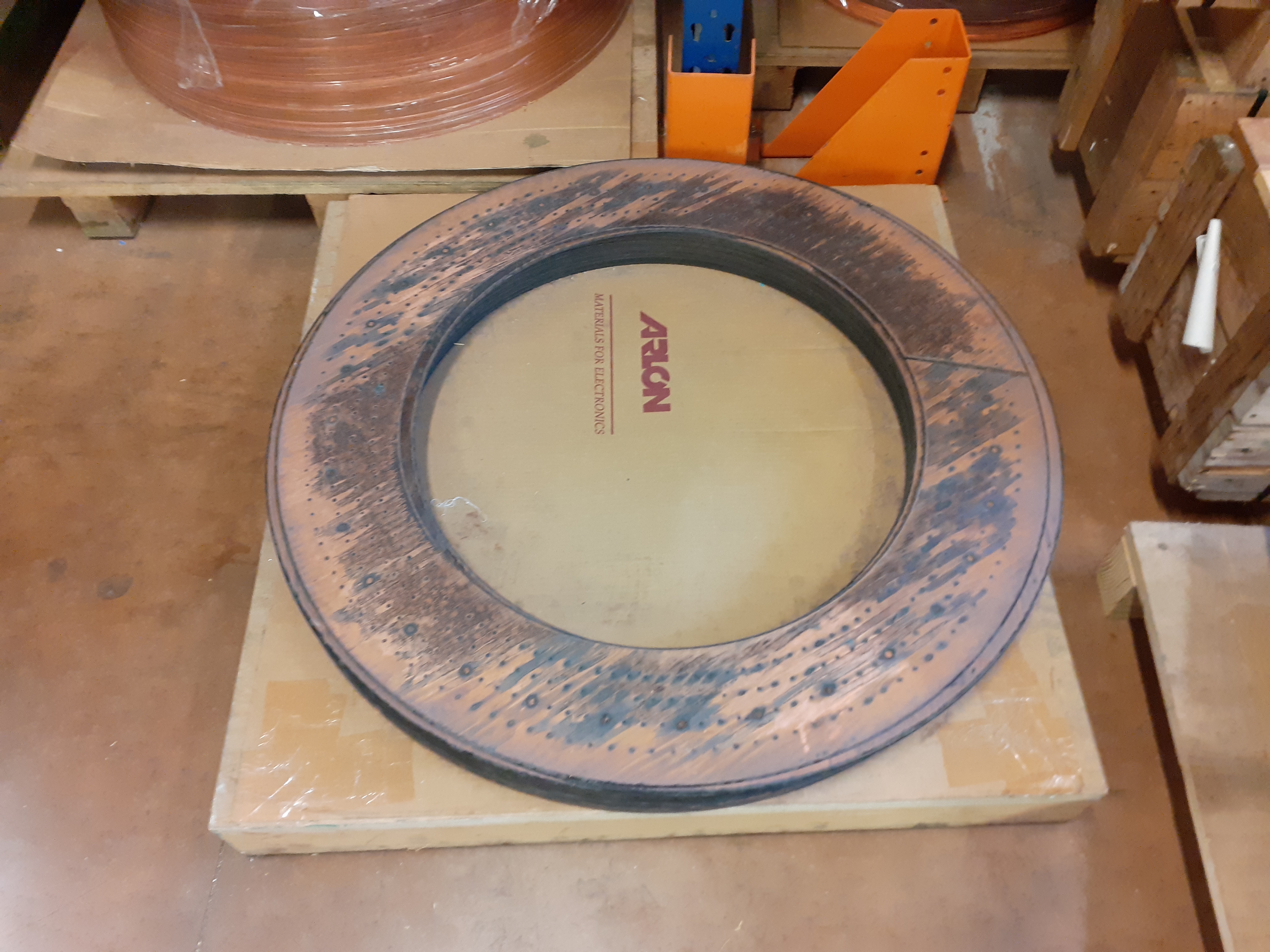

Old circle of copper
|
The resistive magnet reach the largest magnetic field (the most is \(37 \, T\)) but are most cost in energy. The laboratory have an electrical installation of \(20000 \, MWatt\) which converts the alternate current of the electrical network by continuous current to feed electro-magnets.
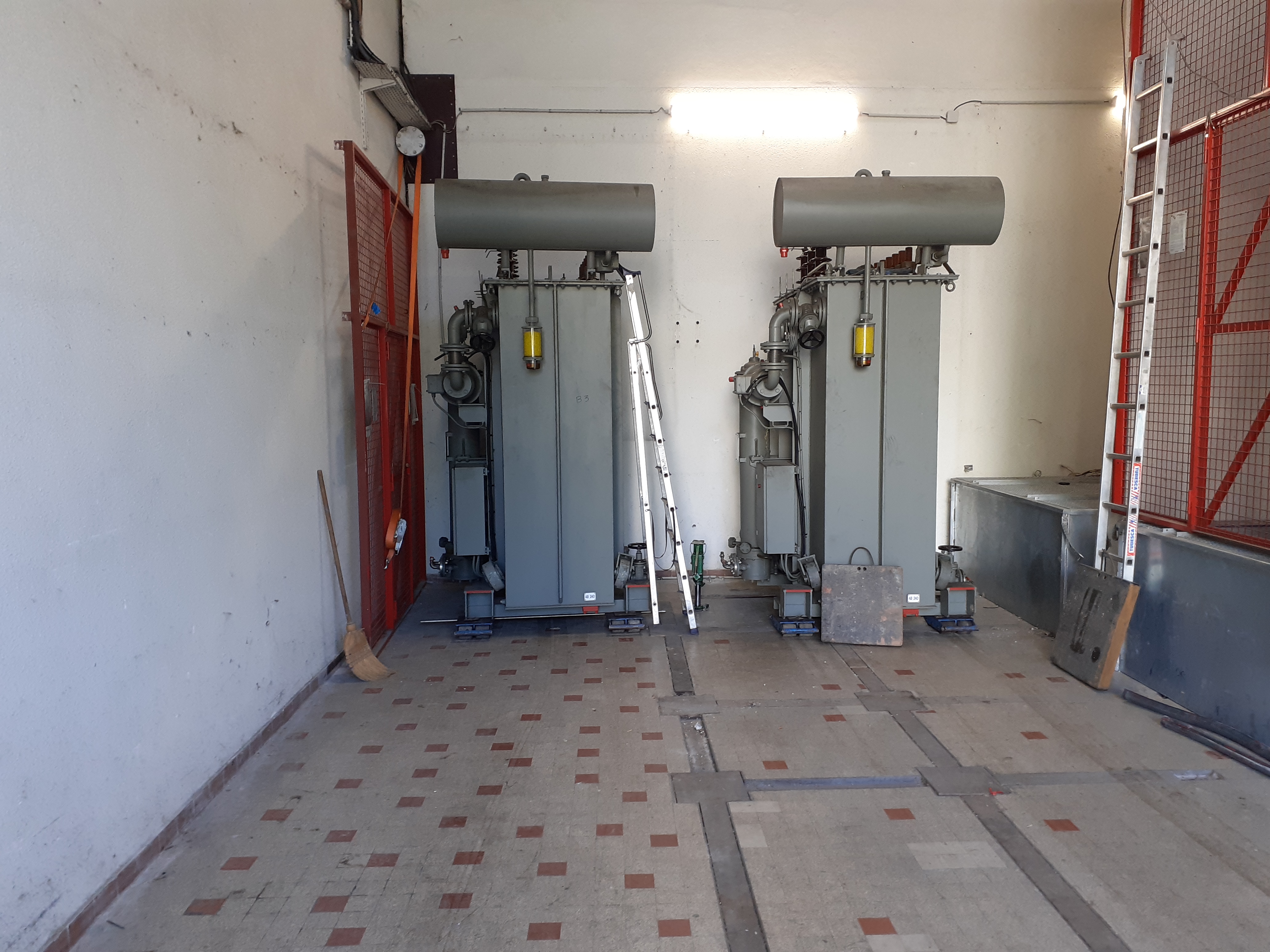

Electrical transformer
|

Electrical transformer
|
Superconductor magnet, it composed by superconductor matters, it’s matters without electrical resistance. It does not give off heat but it loses its property of non-resistance for great temperature. This type of magnet need cooling at very small temperature with nitrogen liquid or nitrogen liquid. The superconductor matters loses its property of non-resistance for great magnetic field. The superconductor magnet is less costly in energy but not exceed \(25 \, T\) and have little space of experiments.
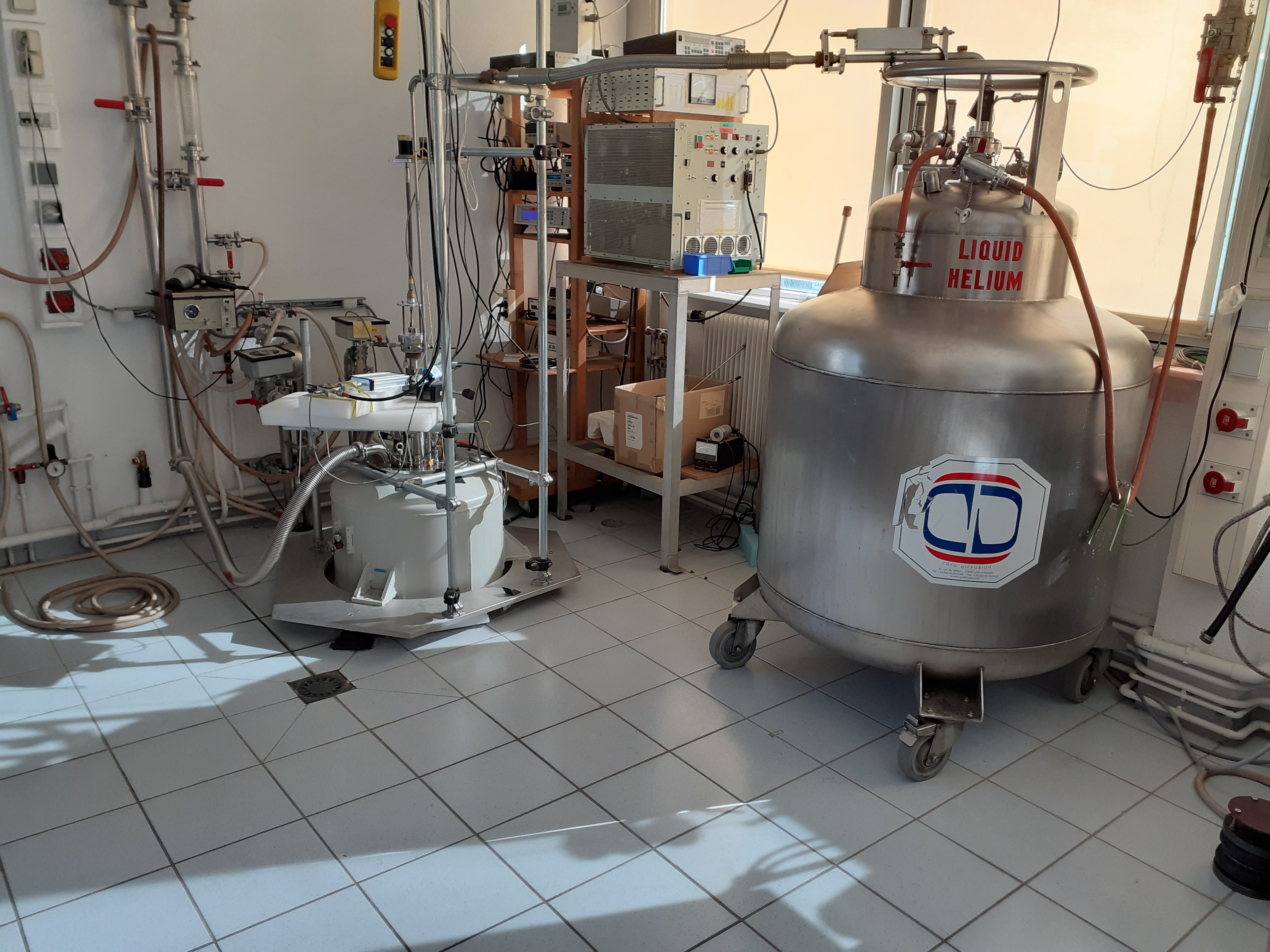

A superconducting magnet (to the left) with its liquid helium cylinder (to the right)
|

A interior of superconducting
|