Test of Maxwell Quasi Static with gauge condition on Two Torus
1. Introduction
In this page, I present the test case of Maxwell Quasi Static Problem with the A-V Formulation with gauge condition for a geometry of torus surrounded by air.
2. Run the calculation
The command line to run this case is :
mpirun -np 32 feelpp_toolbox_coefficientformpdes --config-file=mqs.cfg --cfpdes.gmsh.hsize=5e-3
3. Data Files
The case data files are available in Github here :
-
CFG file - Edit the file
-
JSON file - Edit the file
-
GEO file - Edit the file
4. Equation
Thus \(\Omega\) the domain, comprising the conductor (or superconductor) domain \(\Omega_c\) and non conducting materials \(\Omega_n\) (\(\mathbf{J} = 0\)) like air. Let \(\Gamma = \partial \Omega\) the bound of \(\Omega\), \(\Gamma_c = \partial \Omega_c\) the bound of \(\Omega_c\), \(\Gamma_D\), \(\Gamma_{Dc}\) the bound with Dirichlet boundary condition and \(\Gamma_N\), \(\Gamma_{Nc}\) the bound with Neumann boundary condition, such that \(\Gamma = \Gamma_D \cup \Gamma_N\) and \(\Gamma_c = \Gamma_{Dc} \cup \Gamma_{Nc}\).
We introduce :
-
Magnetic potential field \(\mathbf{A}\) : the magnetic field writes \(\textbf{B} = \nabla \times \textbf{A}\)
-
Electric potential scalar : \(\nabla V = - \textbf{E} - \frac{d \textbf{A}}{d t}\)
We have the conditions :
-
\(\nabla \cdot \mathbf{A} = 0\)
-
\(\mu\) is independant of space
We want to resolve the electromagnetism problem ( with \(\mathbf{A}\) and \(V\) the unknows) :
This equation is obtain from the A-V Formulation with the gauge conditions. The detail calculus are in page MQS + gauge condition.
5. Geometry
The geometry is two tores of conductor surrounded by air.
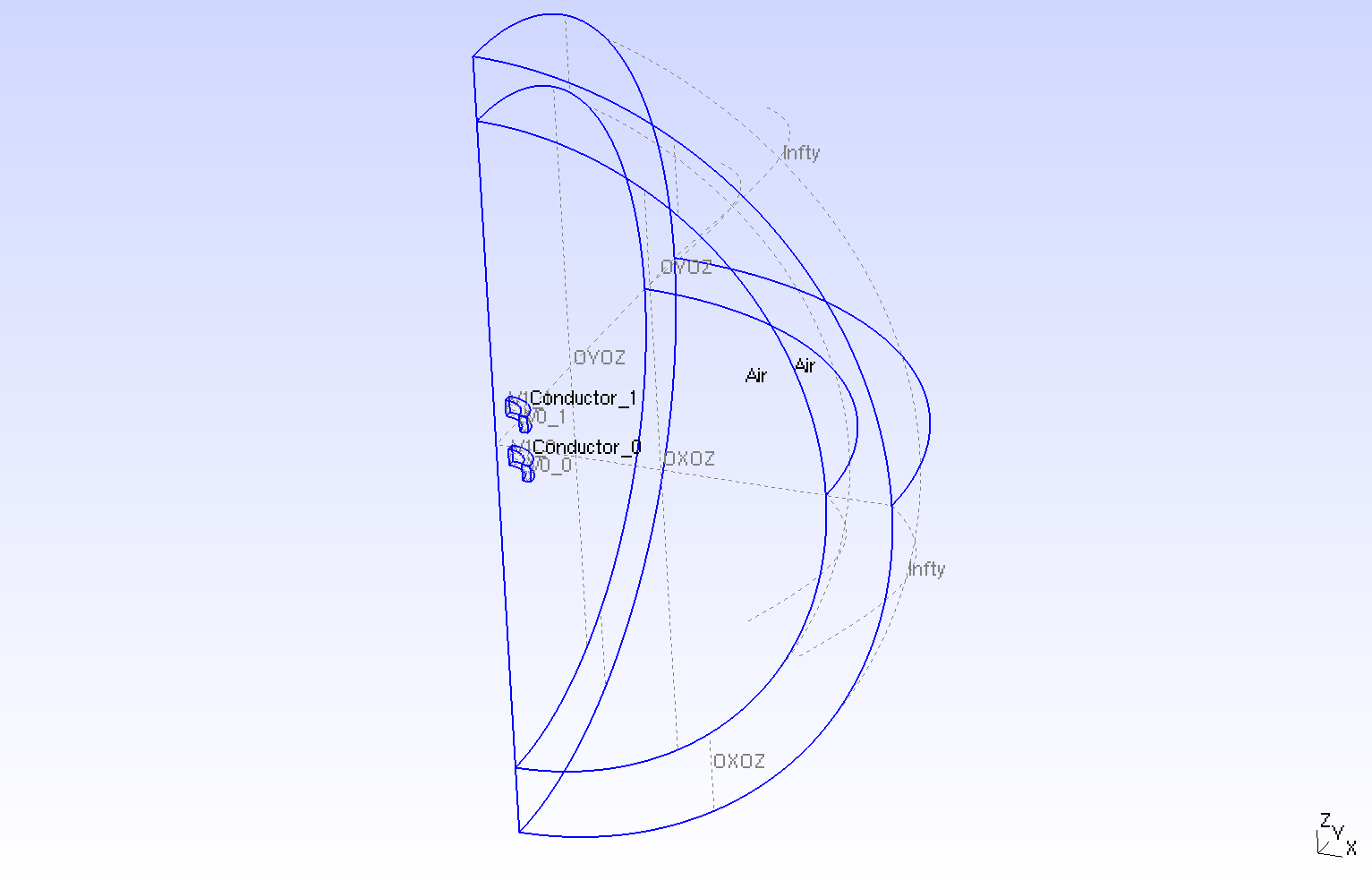
Geometry
|
.png)
Geometry loop on Conductors
|
The geometrical domains are :
-
Conductor_0: the first torus, it is composed of conductive materials-
V0_0: enter of electrical potential -
V1_0: exit of electrical potential
-
-
Conductor_1: the second torus, it is composed of conductive materials-
V0_1: enter of electrical potential -
V1_1: exit of electrical potential
-
( Conductor_0 \(\cup\) Conductor_1 \( = \Omega_c\) and V0_0 \(\cup\) V1_0 \(\cup\) V0_1 \(\cup\) V1_1 \( = \Gamma_{Dc}\))
-
air(\(\Omega/\Omega_c\)) : the air surroundConductor-
OXOZ: \(OxOz\) plan -
OYOZ: \(OyOz\) plan -
Infty: the rest of bound ofAir
-
Symbol |
Description |
value |
unit |
\(r_{int}\) |
interior radius of tores |
\(75e-3\) |
m |
\(r_{ext}\) |
exterior radius of tores |
\(100.2e-3\) |
m |
\(z_1\) |
half-height of torus |
\(25e-3\) |
m |
\(r_{infty}\) |
radius of infty border |
\(5*r_{ext}\) |
6. Initial/Boundary Conditions
We impose the Dirichlet boundary conditions :
-
For \(V\) equation :
-
On
V0_0andV0_1: \(V=0\) -
On
V1_0: \(V = \frac{1}{4} \left\{ \begin{matrix} \frac{t}{0.1} \text{ on } 0s \leq t < 0.1s \\ 1 \text{ on } 0.1s \leq t < 0.5s \\ t \text{ on } 0.5s \leq t \end{matrix} \right. \) -
On
V1_1: \(V = \frac{1}{4} \left\{ \begin{matrix} \frac{t}{0.1} \text{ on } 0s \leq t < 0.1s \\ 1 \text{ on } 0.1s \leq t < 0.7s \\ t \text{ on } 0.7s \leq t \end{matrix} \right. \)
-
-
For \(\mathbf{A}\) :
-
On
OXOZ,V0_0andV0_1: \(A_x = A_z = 0\), we want \(\mathbf{A}\) orthogonal toOXOZandV0 -
On
OYOZ,V1_0andV1_1: \(A_y = A_z = 0\), we want \(\mathbf{A}\) orthogonal toOYOZandV1 -
Infty: We approximate the problem,Inftyis the physical infty thus \(\mathbf{B}=0\) atInftythus \(\mathbf{A} = 0\).
-
We initialize at \(t=0s\) :
-
\(V = 0\)
-
\(\mathbf{A} = 0\)
On JSON file, the boundary conditions are writed :
"BoundaryConditions":
{
"magnetic":
{
"Dirichlet":
{
"Infty":
{
"expr":"{0,0,0}"
}
},
"Dirichlet_x":
{
"mydir_x":
{
"markers":["V0_0","V0_1","OXOZ"],
"expr":0
}
},
"Dirichlet_y":
{
"mydir_y":
{
"markers":["V1_0","V1_1","OYOZ"],
"expr":0
}
},
"Dirichlet_z":
{
"mydir_z":
{
"markers":["V0_0","V0_1","OXOZ","V1_0","V1_1","OYOZ"],
"expr":0
}
}
},
"electric":
{
"Dirichlet":
{
"V0_0":
{
"expr":"materials_Conductor_0_V0:materials_Conductor_0_V0"
},
"V0_1":
{
"expr":"materials_Conductor_1_V0:materials_Conductor_1_V0"
},
"V1_0":
{
"expr":"materials_Conductor_0_V1:materials_Conductor_0_V1"
},
"V1_1":
{
"expr":"materials_Conductor_1_V1:materials_Conductor_1_V1"
}
}
}
}
For initial condition, we write nothing in JSON, by default the application put zeros on initialization.
7. Weak Formulation
The weak formulation of A-V Formulation + gauge is :
8. Parameters
The parameters of problem are :
-
On
Conductor:
Symbol |
Description |
Value |
Unit |
\(V0\) |
scalar electrical potential on |
\(0\) |
\(Volt\) |
\(V1\) |
scalar electrical potential on |
\(\frac{1}{4} \left\{ \begin{matrix} t \ \text{on} \ 0s \leq t < 1s \\ 1 \ \text{on} \ 1s \leq t < 20s \\ 0 \ \text{on} \ 20s \leq t \end{matrix} \right.\) |
\(Volt\) |
\(\sigma\) |
electrical conductivity |
\(58e6\) |
\(S/m\) |
\(\mu=\mu_0\) |
magnetic permeability of vacuum |
\(4\pi.10^{-7}\) |
\(kg \, m / A^2 / S^2\) |
-
On
Air:
Symbol |
Description |
Value |
Unit |
\(\mu=\mu_0\) |
magnetic permeability of vacuum |
\(4\pi.10^{-7}\) |
\(kg \, m / A^2 / S^2\) |
9. Coefficient Form PDEs
We use the application Coefficient Form PDEs. The coefficient associate to Weak Formulation are :
-
On
Conductor_0andConductor_1:
Coefficient |
Description |
Expression |
|
damping or mass coefficient |
\(\sigma\) |
|
diffusion coefficient |
\(\frac{1}{\mu}\) |
|
source term |
\(- \sigma \nabla V \) |
|
damping or mass coefficient |
\(\sigma\) |
|
source term |
\(\sigma \, \frac{d \mathbf{A}}{d t}\) |
-
On
Air(the lectrical potential isn’t computed onAir) :
Coefficient |
Description |
Expression |
|
diffusion coefficient |
\(\frac{1}{\mu}\) |
On JSON file, the coefficients are writed :
"Materials":
{
"Conductor_0":
{
"V0":0,
"V1":"1/4*(t/(0.1)*(t<(0.1))+(t<(0.5))*(t>(0.1))):t",
"sigma":58e6, // S.m-1
"mu":"4*pi*1e-7", // kg.m/A2/S2
"magnetic_d":"sigma:sigma",
"magnetic_c":"1/mu:mu",
"magnetic_f":"{-sigma*electric_grad_V_0,-sigma*electric_grad_V_1,-sigma*electric_grad_V_2}:sigma:electric_grad_V_0:electric_grad_V_1:electric_grad_V_2",
"electric_c":"sigma:sigma",
"electric_gamma":"{sigma*magnetic_dA_dt_0,sigma*magnetic_dA_dt_1,sigma*magnetic_dA_dt_2}:sigma:magnetic_dA_dt_0:magnetic_dA_dt_1:magnetic_dA_dt_2"
},
"Conductor_1":
{
"V0":0,
"V1":"1/4*(t/(0.1)*(t<(0.1))+(t<(0.7))*(t>(0.1))):t",
"sigma":58e6, // S.m-1
"mu":"4*pi*1e-7", // kg.m/A2/S2
"magnetic_d":"sigma:sigma",
"magnetic_c":"1/mu:mu",
"magnetic_f":"{-sigma*electric_grad_V_0,-sigma*electric_grad_V_1,-sigma*electric_grad_V_2}:sigma:electric_grad_V_0:electric_grad_V_1:electric_grad_V_2",
"electric_c":"sigma:sigma",
"electric_gamma":"{sigma*magnetic_dA_dt_0,sigma*magnetic_dA_dt_1,sigma*magnetic_dA_dt_2}:sigma:magnetic_dA_dt_0:magnetic_dA_dt_1:magnetic_dA_dt_2"
},
"Air":
{
"physics":"magnetic",
"mu":"4*pi*1e-7", // kg.m/A2/S2
"magnetic_c":"1/mu:mu"
}
}
10. Numeric Parameters
This section show the parameters used to compute the simulation.
-
Size of mesh :
-
On
Conductor: \(0.5 \, mm\) -
On
Infty: \(100 \, mm\)
-
-
Time Parameters :
-
Time step : \(0.1 \, s\)
-
Initial Time : \(0 \, s\)
-
Final Time : \(22 \, s\)
-
-
Element type : \(P1\)
-
Solver : automatic
-
Number of CPU core : \(32\)
Mesh of Geometry
|
11. Results
11.1. Magnetic Fields
I plot the horizontal magnetic field by time on point \((0,0,0)\).
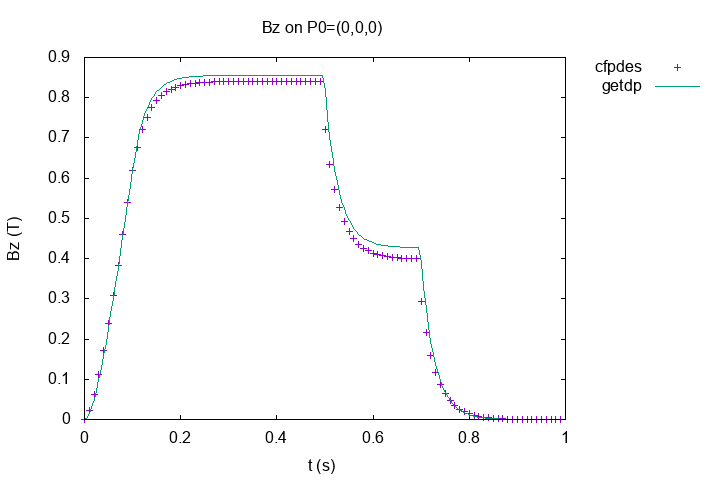
Horizontal Magnetic Field \(B_z (T)\) by time
|
We can see the four step :
-
the ramp for the two tensions
-
the tray for the two tensions
-
the tray for the tension \(U_1\) and the tray at 0 for the tension \(U_0\)
-
the tray for the tray at 0 for the tensions \(U_0\) and \(U_1\)
11.2. Intensities
The analytical solve of intensities is computed by python3’s script : Edit the file, with the formula :
And the values :
Symbol |
Description |
Value |
Unit |
\(R_0\) |
resistance of |
\(7.479339e-06\) |
\(Ohm\) |
\(R_1\) |
resistance of |
\(7.479339e-06\) |
\(Ohm\) |
\(L_0\) |
auto-inductance of |
\(1.920400e-07\) |
\(Henry\) |
\(L_0\) |
auto-inductance of |
\(1.920400e-07\) |
\(Henry\) |
\(M_{01}\) |
inductance from |
\(1.705000e-08\) |
\(Henry\) |
\(M_{10}\) |
inductance from |
\(1.705000e-08\) |
\(Henry\) |
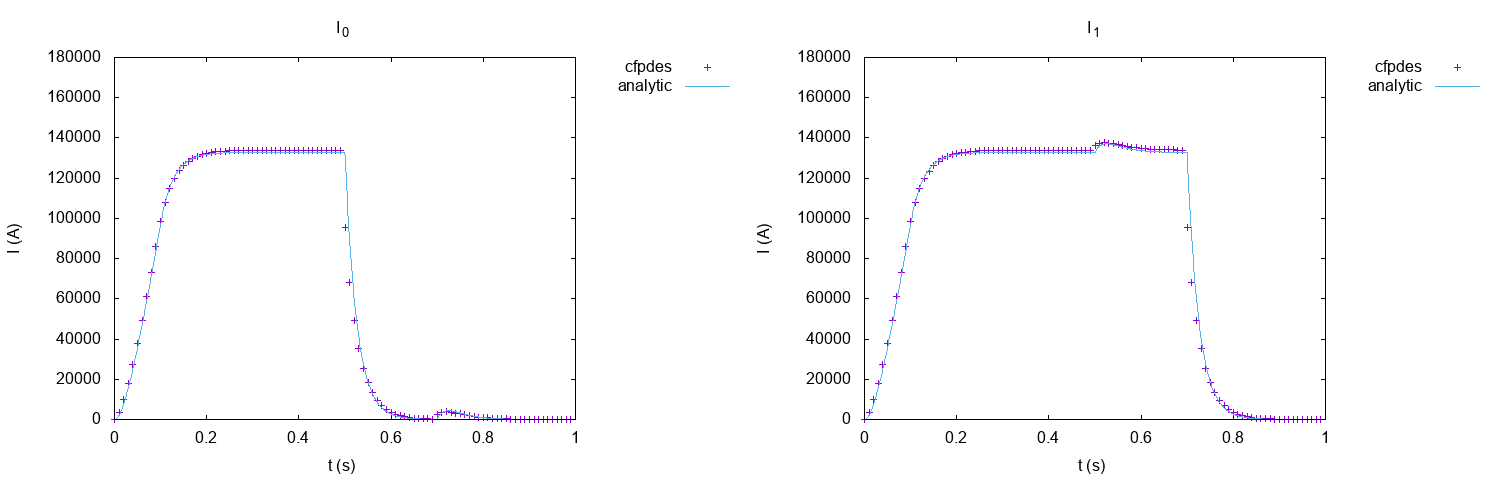
Intensities : Comparison between numerical and analytical results
|
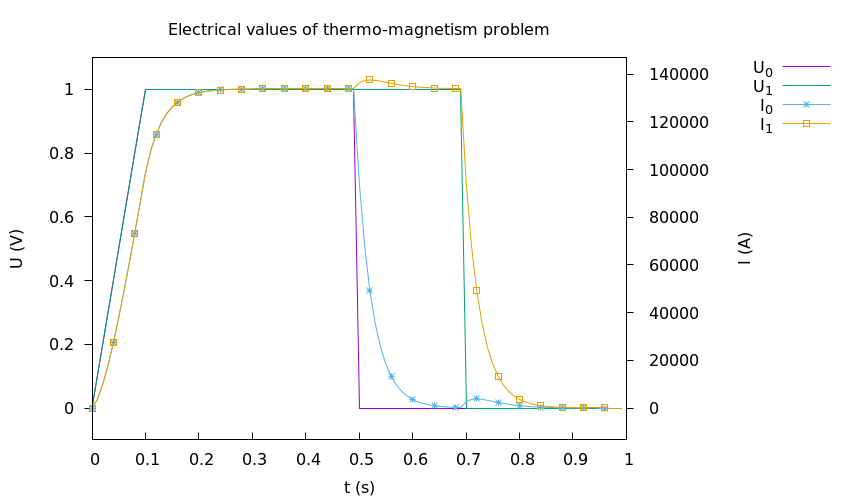
Figure 1. Intensities \(I_i (A)\) and Tensions \(U_i(V)\), caption=
|
The intensities follow the tensions like for 1-Torus problem with the four step (ramp, trays and cuts). But, we can see little peaks. This peak on one intensity appears when the tension of other conductor is cut. This phenomena is called Electromagnetism Induction.
The Electromagnetism Induction is the production of an electromotive force across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
With the equation of Maxwell-Faraday :
We can see, with time variation of magnetic field \(\mathbf{B}\), we have creation of electrical field. For us case, when we cut the tension for one conductor, we have great time variation of magnetic field thus the other conductor answer by Maxwell-Faraday equation with creation of electrical field and current. When the magnetic field is at zeros, is phenomena disapears.